
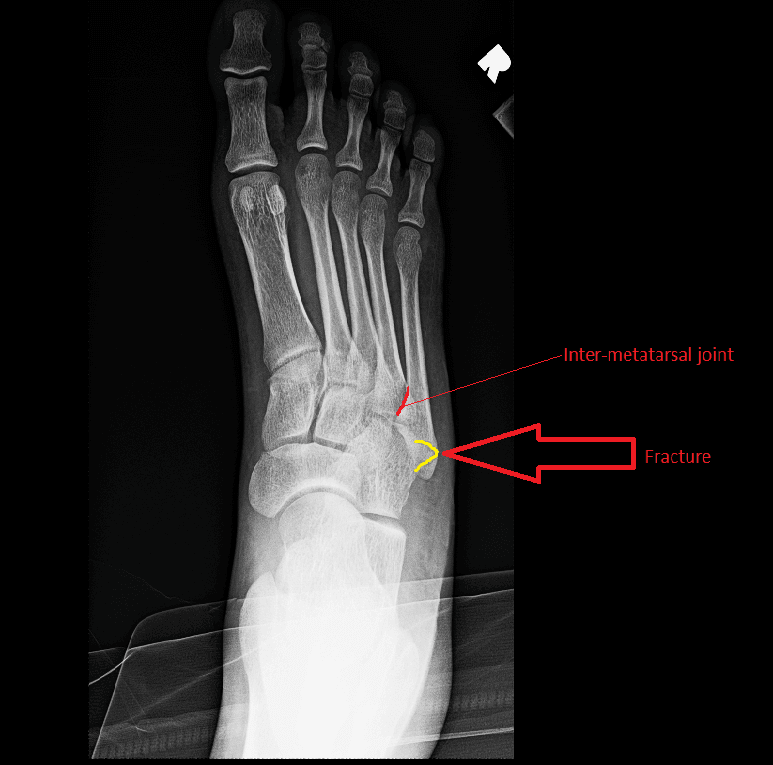
Asymptomatic non-union may be slightly more common but does not necessarily require any treatment. Symptomatic non-union is very rare with these fractures. However, radiographic evidence for union may lag behind resolution of clinical symptoms. Regardless of any specific treatment modality, majority of these fractures heal uneventfully within 6 to 8 weeks. A comparative cohort study of 39 patients (23 casts, 16 removable boots) showed a shorter mean time to preinjury function and less pain with boots compared to cast. Some studies have reported successful outcomes with a removable cast. An RCT including 60 avulsion fractures reported that patients treated with a soft dressing recovered significantly faster than those treated in a cast (33 days vs 46 days). Type III: non-unions with obliteration of the intramedullary canalĬonservative treatment ranges from a soft bandage to a light weight cast. Type II: delayed fracture healing with a widened fracture line and intramedullary sclerosis Type I: acute fractures without intramedullary sclerosis Torg and colleagues defined three categories of fifth metatarsal base fractures based on healing potential and radiographic appearance: Type IIIB: intra-articular tuberosity avulsions Type IIIA: extra-articular tuberosity avulsions Type II: chronic metadiaphyseal fractures with either a clinical symptoms or radiologic evidence of stress reaction Type IB: acute, comminuted metadiaphyseal fractures Type IA: acute, undisplaced, metadiaphyseal fractures Zone III - the proximal diaphyseal region - stress fracture.ĭeLee and colleagues separated proximal fifth metatarsal fractures into: Zone II - the metadiaphyseal region - Jones fracture (at the level of 4th/5th intermetatarsal joint) Zone I - the tuberosity - avulsion fracture (more than 90% fractures in their study) Lawrence and Botte divided the proximal fifth metatarsal into three distinct fracture zones: Fractures at the junction of metaphysis and diaphysisĪlthough commonly used, this categorization carries some ambiguity because the precise anatomic location of the physeal junctions is not well defined. Fifth metatarsal fractures have been classically categorized based on location:Ģ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
